

Next: Spectral reading
Up: Speech Enhancement Summaries
Previous: Rezayee's and Gazor's noise
The frequency-domain version of the Wiener filter is
![$y[n]$](img73.png) is processed at L-frame intervals. Averaging spectra over the background region gives an estimate to the background spectral density,
is processed at L-frame intervals. Averaging spectra over the background region gives an estimate to the background spectral density,
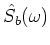 .
The desired signal spectrum is obtained by applying the Wiener filter from the previous frame to the current frame noisy spectrum
.
The desired signal spectrum is obtained by applying the Wiener filter from the previous frame to the current frame noisy spectrum
which is then used to update the Wiener filter for the next frame:
The Wiener filter can be made to vary more smoothly from frame to frame
where
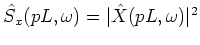 .
The temporal smoothing introduced by the adaptive Wiener filter blurs transient and rapidly-varying speech components.
Use instead
.
The temporal smoothing introduced by the adaptive Wiener filter blurs transient and rapidly-varying speech components.
Use instead
as a measure of the ``degree of stationarity''.
When the spectrum is changing rapidly, little temporal smoothing is applied whereas when the spectrum is stationary, smoothing improves the spectral estimate.
where
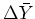 is the average spectral derivative over the background and reduces the noise presence.
is the average spectral derivative over the background and reduces the noise presence.


Next: Spectral reading
Up: Speech Enhancement Summaries
Previous: Rezayee's and Gazor's noise
Vinesh Bhunjun
2004-09-17
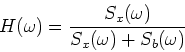
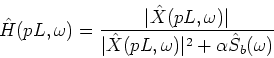
![\begin{displaymath}
\Delta Y(pL)=\left[ \frac{1}{\pi} \int_{0}^{\pi} \vert Y(pL,\omega)-Y((p-1)L,\omega)\vert^2 d \omega \right]^{1/2}
\end{displaymath}](img79.png)