

Next: Spectral Change and Adaptive
Up: Speech Enhancement Summaries
Previous: Projection error measure
Ephraim and Van Trees [4] assume
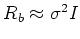 .
Rezayee and Gazor assume that the noise and speech eigenvectors are approximately equal.
Then
.
Rezayee and Gazor assume that the noise and speech eigenvectors are approximately equal.
Then
where
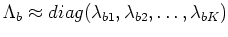 .
This is especially true if
.
This is especially true if 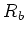 is close to Toeplitz.
is close to Toeplitz.
Noise samples taken from the most recent silent period are projected onto the current signal eigenvectors to obtain the variance of each noise component.
Vinesh Bhunjun
2004-09-17